Table of contents
WATER REUSE IN THE INDUSTRIAL SECTOR
The concept of water reuse involves reusing water in the same activity in which it was used or in a different activity.
The current shortage, coupled with the high cost of water supply and discharge, is forcing industries to make the most of the water from their processes, making water reuse in the industrial sector an increasingly widespread practice.
WHY REUSE PROCESS WATER?
Among the benefits of process water reuse for industries are the reduction of the water footprint, economic savings and reduced wastewater generation.
In addition, it is important to note that reuse guarantees the availability of water in the face of water supply limitations and problems, providing an alternative source of process water that promotes a circular economy.
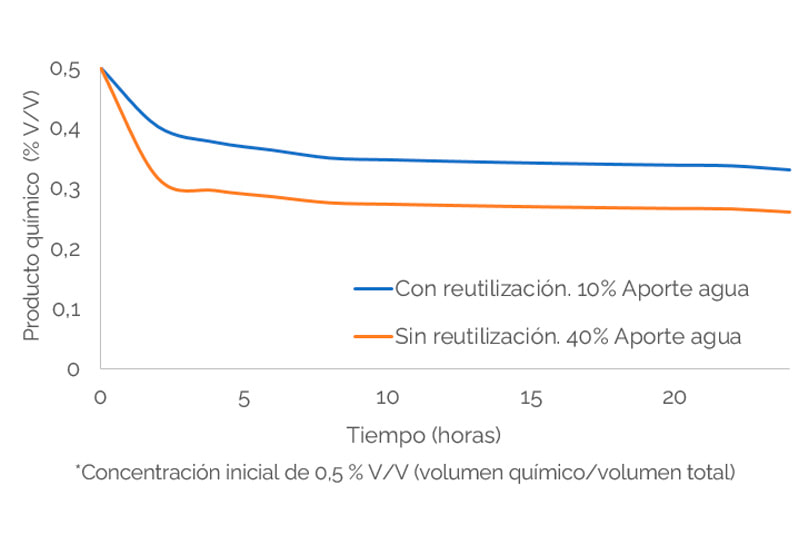
- Reduction of water and chemical reagent consumption
Reusing process water leads to a reduction in the consumption of feed water and chemical reagents used in the process, such as coolants, oxidizers or disinfectants .
Since the feed water has no residual chemical content, unlike reused water, as the water input to the process is reduced, the amount of chemical required to maintain its concentration constant decreases.
- Decrease in the amount of wastewater generated
Reused process water is water that is not sent to the WWTP (Industrial Wastewater Treatment Plant) and is therefore not considered or treated as wastewater.
Reuse of process water allows not to saturate the WWTPI, and at the same time:
- Increases scrubbing performance, helping the scrubber not to exceed the design load.
- Increases industrial production capacity with the same WWTPI.
- Reduces the amount of the discharge control fee.
IMPORTANCE OF THE TECHNOLOGY APPLIED IN PROCESS WATERS
For an industry it is key to know what reuse needs its water requires. These needs will be determined by the application in which the water is to be used.
For example, if we want to reuse process water in auxiliary systems such as cooling circuits and boilers, it will be essential to remove suspended solids and turbidity from the water, and to study whether it is necessary to lower the conductivity.
For processes that seek to reuse water for nozzle protection, spraying or flushing for cleaning, it will be essential to focus the filtration on removing particles larger than the size of the nozzle, preventing it from being clogged.
Other processes that allow water to be reused are the washing of industrial machinery, cleaning systems or washing tubs in the agri-food industry. In both processes, we can obtain clarified water through a double filtration, with a coarser solids stage and a second stage of fine solids.
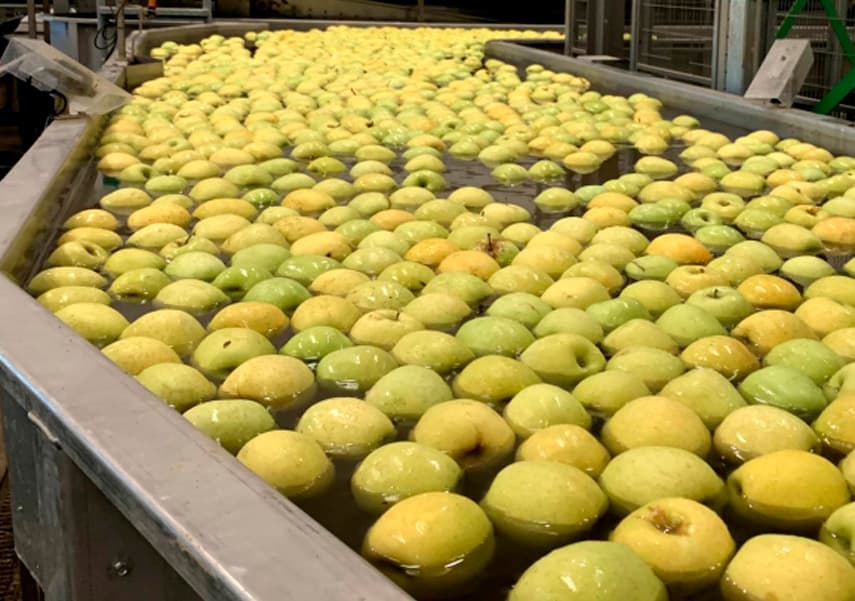

Another example is the chemical industry, which can reduce its consumption of mains and waste water by up to 30% by using reused water in cooling, dilution and cleaning processes, thus achieving cost reductions and significant water savings.
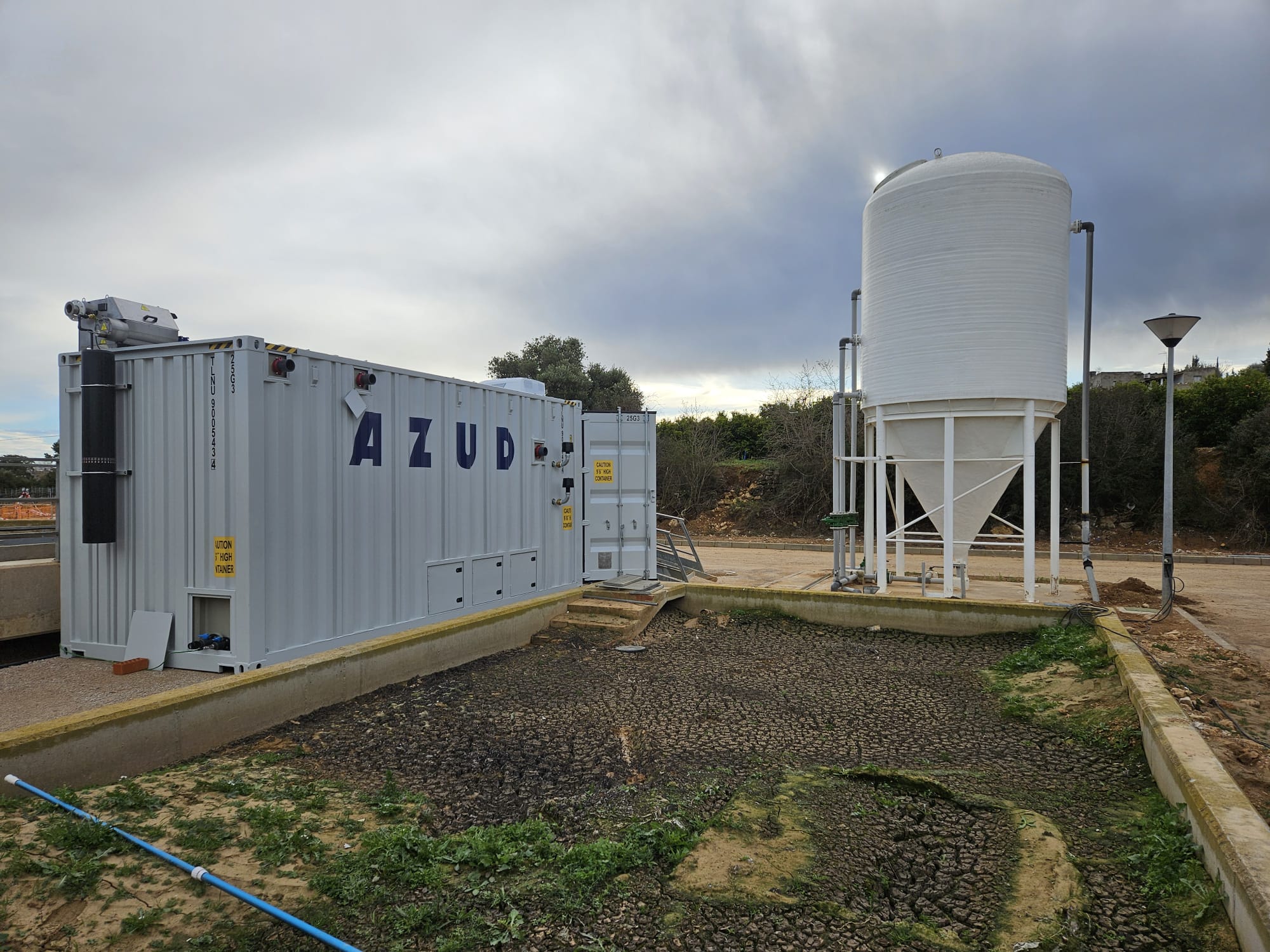
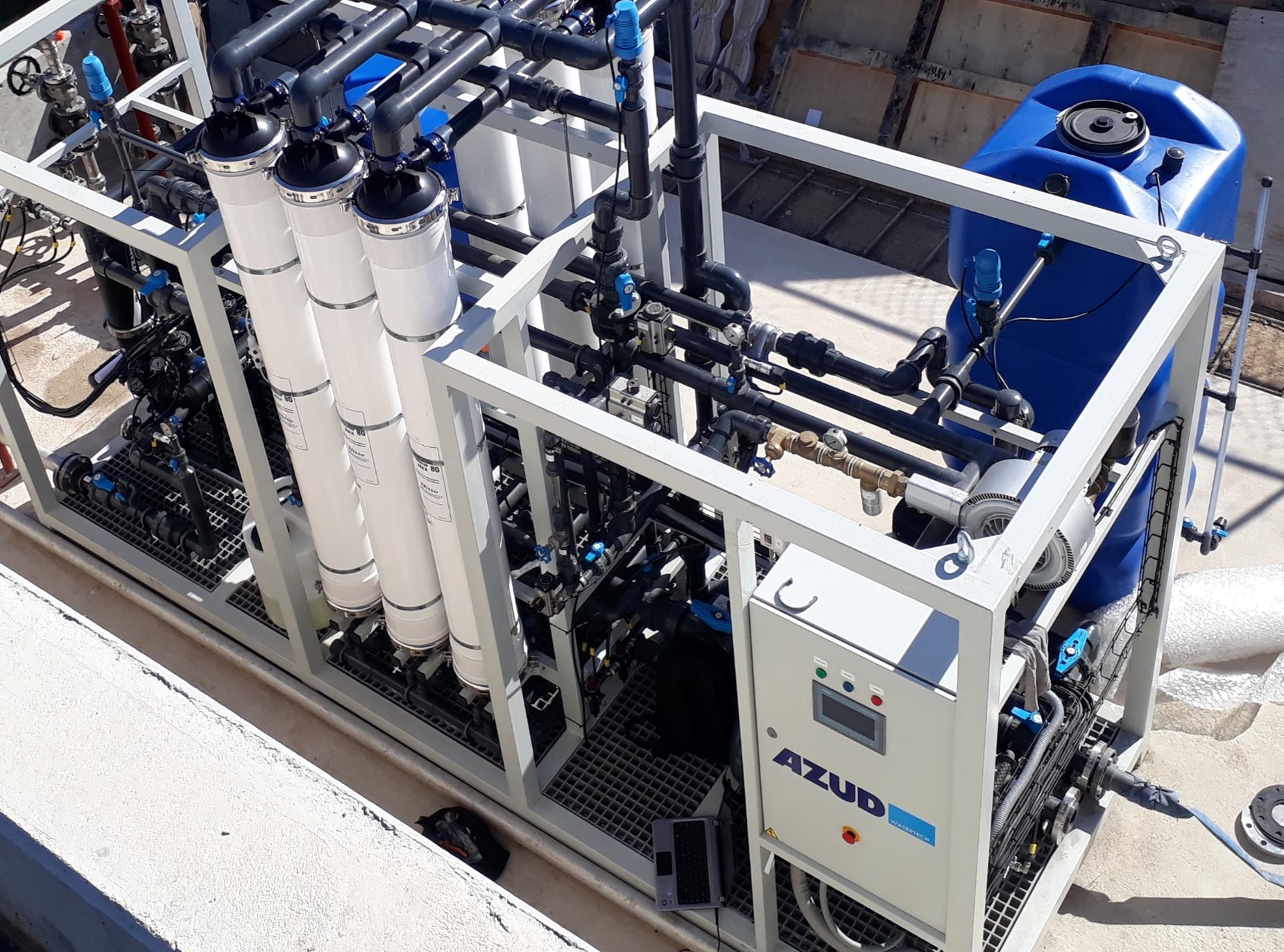
WEIR SOLUTIONS FOR PROCESS WATER REUSE
At AZUD we are aware of the large consumption of water in many industrial processes and we want to offer solutions that guarantee its correct reuse.
AZUD HELIX AUTOMATIC AA disc filtration systems, with their double surface and depth filtration effect, allow the removal of suspended organic and inorganic particles contained in the process water below the filtration degree, thus guaranteeing their absence in the reused water.
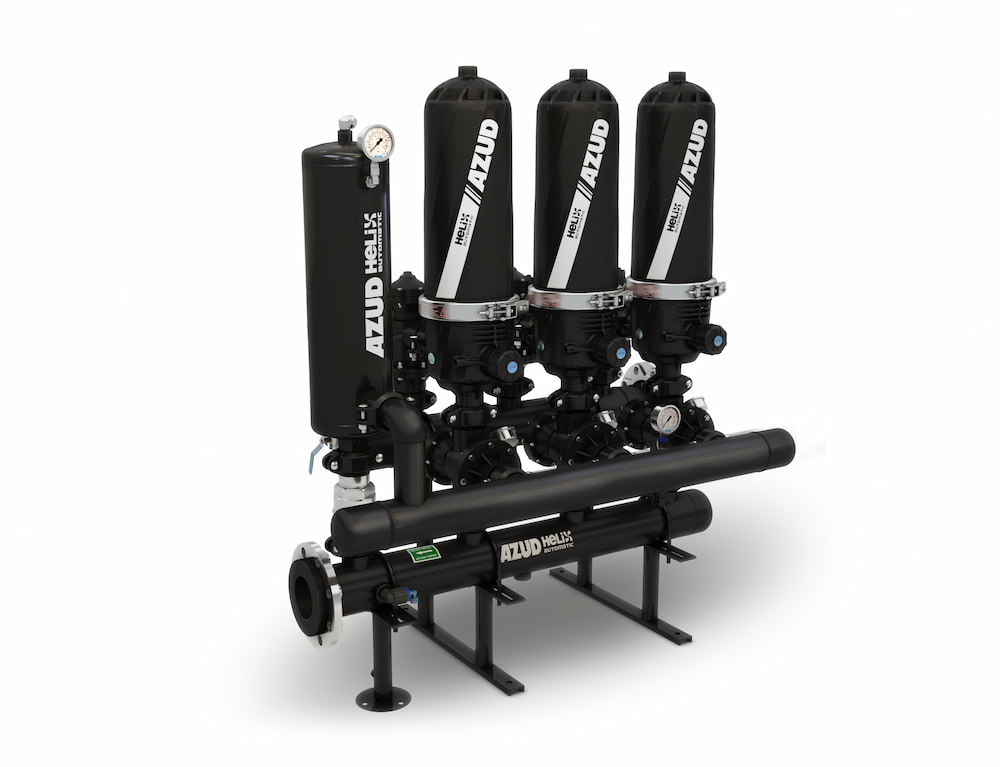

Outstanding for their reliability, they guarantee an uninterrupted supply of filtered water thanks to the sequential flushing of each filter element.
Its AA system contributes to reducing the water footprint by requiring only 10 liters of water for backwashing per filter element. In addition, it allows to reduce the frequency of maintenance operations thanks to the effectiveness with which cleaning is carried out.