Table of contents
In the constant quest to reduce harmful nitrogen oxide (NOx) emissions from diesel engines, AdBlue has emerged as a key ally. This liquid composed of urea and water has not only become a standard for reducing pollution, but has also revolutionized the way diesel vehicles comply with environmental regulations.
What is AdBlue?
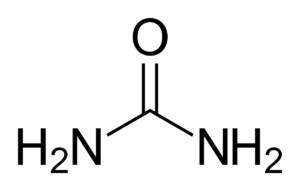
AdBlue is a highly purified colorless liquid that incorporates demineralized water and urea in a proportion of 32.5%. Its main application is in diesel engines, and beyond European borders, it is known under various names, such as DEF, ARLA 32 or AUS 32.
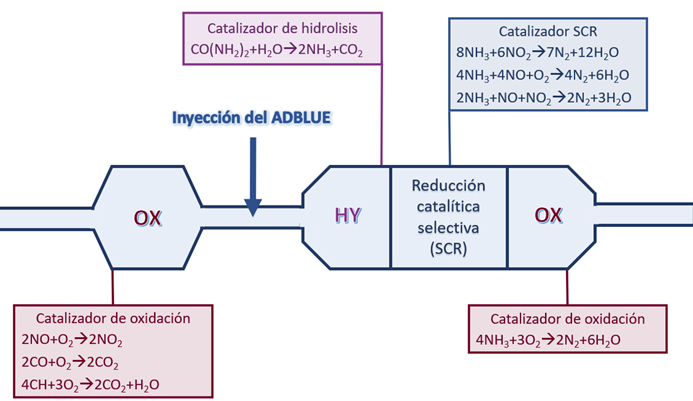
This liquid is injected into the catalyst of the SCR (Selective Catalytic Reduction) system, triggering a chemical reaction capable of reducing NOx emissions in the exhaust gases generated during the combustion process.
When AdBlue comes into contact with the hot gases, it releases ammonia, a substance that facilitates the reaction in the catalytic converter, transforming the nitrogen oxides into free nitrogen and water. SCR, an emission control technology, converts nitrogen oxides (NOx) into molecular nitrogen (N2) and water (H2O) by means of a catalyst and a gaseous reductant, usually ammonia, applied to the engine exhaust.
AdBlue manufacturing process
How is AdBlue obtained?
For the manufacture of AdBlue, urea and purified water are required, and this process is carried out in large industrial plants.
Urea is generated by the reaction of ammonia with carbon dioxide, producing urea, water and excess ammonia. CO2 and ammonia gases are recovered and the urea is filtered. Subsequently, to reduce the content of dissolved impurities, it undergoes a process of evaporation and condensation, culminating in the formation of urea granules ready for use.
The next step involves the removal of impurities present in the water. After collection, it is filtered to remove dirt and impurities, and then subjected to a photocatalytic treatment. Using ultraviolet rays and a catalyst, the levels of contaminants and oxygen in the water are reduced.
From the urea manufacturing process, a solution containing 80% urea is extracted and mixed with high quality demineralized water in a static mixer. Once cooled, the solution is continuously analyzed to maintain the proper concentration of AdBlue (32.5% urea and 67.5% water). This balance is achieved by automatically adjusting the water and urea flows to the mixer.
Filtration to produce AdBlue
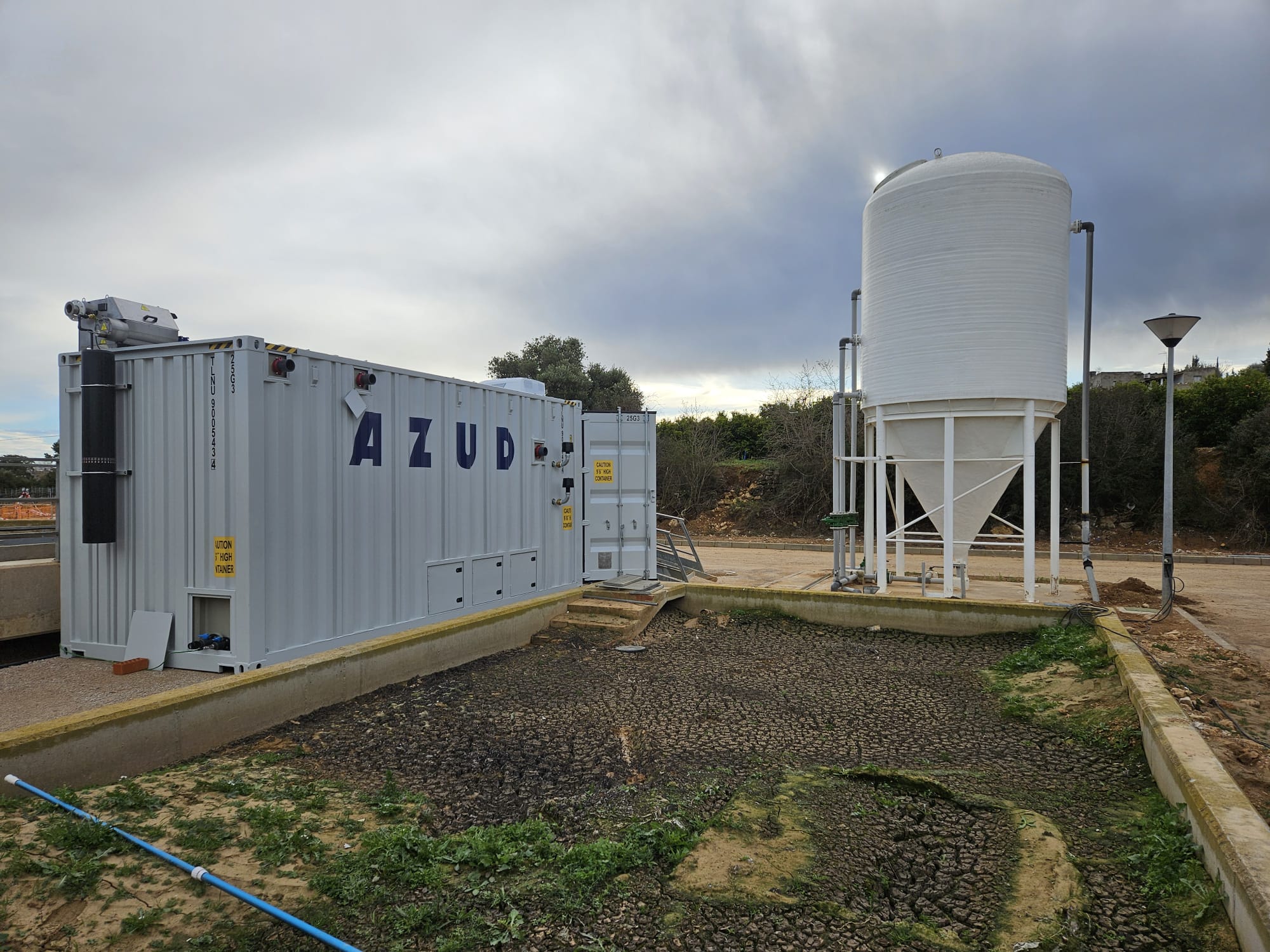
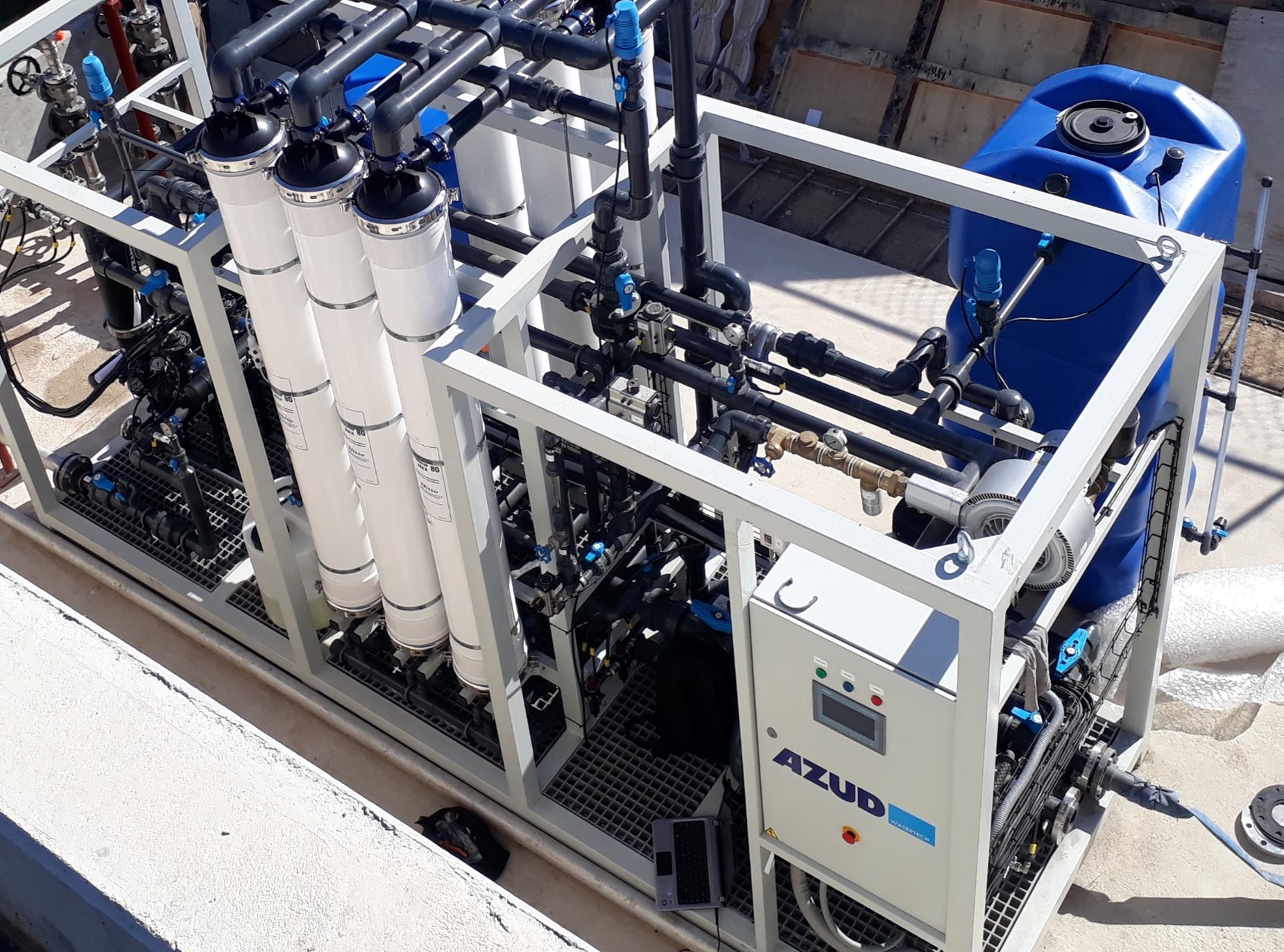
During the production of AdBlue, a filtration process is carried out to remove the inerts present. This is where AZUD filtration solutions come into play and bring numerous benefits when it comes to filtering and reusing process water.
Efficiency in the elimination of impurities.
AZUD filtration systems provide accurate and efficient removal of unwanted particles, resulting in a significant improvement in the quality of the ingredient water, ensuring compliance with the standards required for AdBlue production.
Process optimization.
AZUD filtration systems contribute to the optimal quality of Adblue, improving the purity of the solution and increasing the catalytic capacity of the compound. In addition, AZUD filtration with air-assisted cleaning, AZUD HELIX AUTOMATIC AA
allows maintaining a constant flow rate and quality of filtered Adblue without Adblue consumption during backflushing.
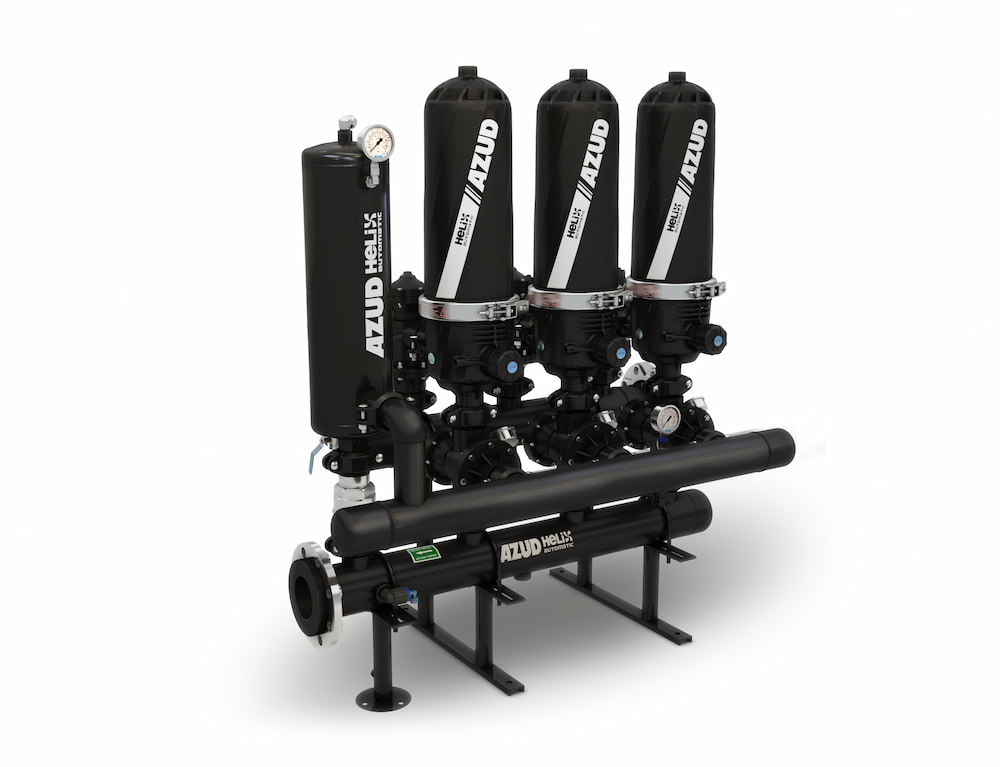

Versatility and adaptability.
These filters, thanks to their materials, have the ability to filter polar compounds without creating films on the plastic discs. This characteristic makes them useful for other chemical solution production processes, such as ethylene glycol, among others, demonstrating their versatility and broad spectrum of application.
The precision and efficiency of AZUD filtration filtration are not only fundamental to the AdBlue manufacturing process, but also extend to other industrial processes, ensuring optimal water treatment and consistent quality in the solutions produced.
If you want to know more about our filtration solutions, do not hesitate to contact our team of experts. We will advise you!





