The fundamental role of fish egg hatcheries
Hatcheries, known as fish egg hatcheries, play a crucial role in aquaculture, where the future of fish stocks is forged. These are the places where fish eggs begin their transformation into fry, and their success depends to a large extent on water treatment, which ensures optimal conditions for hatching and fish growth.
Specialization and purposes of a hatchery
A hatchery specializes in the breeding, hatching and artificial reproduction of early life stages of fish and crustaceans, serving several purposes:
- Food Production: The main focus is the production of fish intended for human consumption.
- Ecosystem conservation and regeneration: Some hatcheries specialize in breeding and releasing endangered or declining fish, thus contributing to the preservation of their populations in the wild.
- Research: They are also scientific research centers where aspects such as fish life cycle, genetics and reproduction are studied.
Process in a hatchery facility
The process in a hatchery facility is a cycle from receipt of fertilized eggs to hatching of the eggs and subsequent transfer of the fry to ponds for continued development.
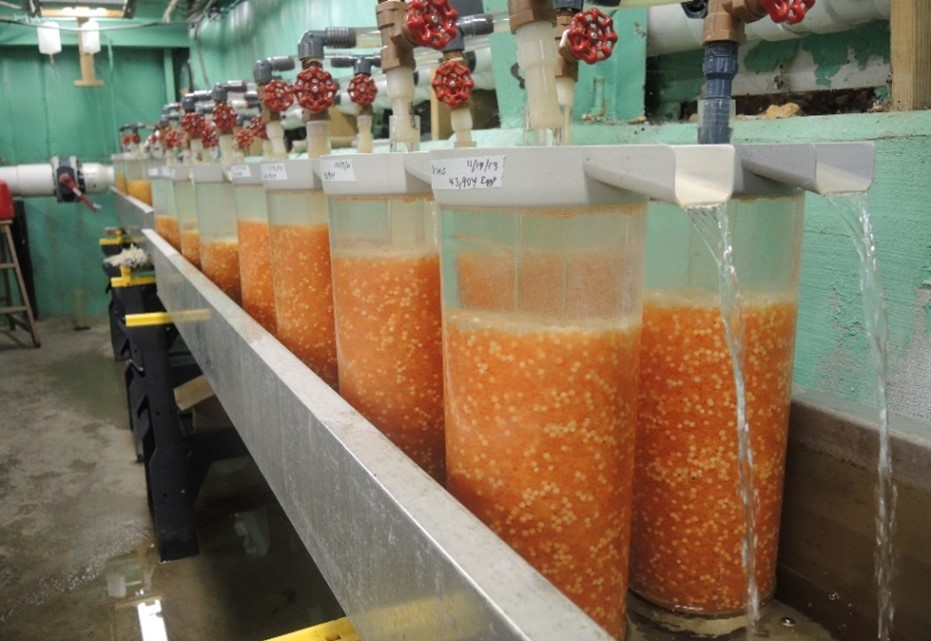
It all starts with the receipt of fertilized eggs, which are usually obtained from brood fish kept in controlled environments. These eggs are transferred to incubation units specifically designed for this stage. These units may consist of tanks, trays or baskets that are filled with water carefully controlled in terms of temperature and water quality.
The water temperature in these hatchery units is maintained within a specific range, optimal for the fish species in question. In addition, to ensure that the embryos receive the necessary oxygen, oxygenation systems are used, which may include air diffusers to introduce oxygen into the water.
Throughout the process, sensors and monitoring systems are installed to constantly monitor water conditions, including measuring temperature, dissolved oxygen levels and other critical parameters.
As the fry emerge from the eggs and begin to grow, they are provided with a specific diet appropriate to their stage of development. Finally, when these fry reach an appropriate size and become robust enough, they are transferred to larger pools to continue their growth.
Critical points in the hatchery operation: water
In these facilities, water is recirculated to reduce water consumption, but this presents a major challenge. During the recirculation process, the water tends to accumulate suspended solids and organic matter, resulting in an increase in water turbidity that can be detrimental to egg development.
There are also other critical variables that require attention, such as oxygen concentration and temperature. Oxygen is essential for respiration of developing species, and these levels can be affected if excessive algal growth occurs, as algae consume the oxygen available in the medium. To ensure healthy oxygen levels, aeration systems are used to ensure that the water is well oxygenated.
Water temperature also plays a crucial role, as it must be kept within a specific range for each type of fish being reared. To achieve this, heating and cooling systems are used to maintain the water temperature at the optimum point for hatching and egg growth.
In addition to these considerations, disinfection methods are applied to prevent diseases and eliminate harmful microorganisms that may affect the developing fish.
The Importance of Water Quality in Hatcheries
In short, it is clear that water quality plays a critical role in the successful incubation and growth of species in hatchery facilities. To achieve these optimum standards, AZUD offers a range of solutions designed to suit each specific case.
AZUD solutions to ensure water quality in hatcheries
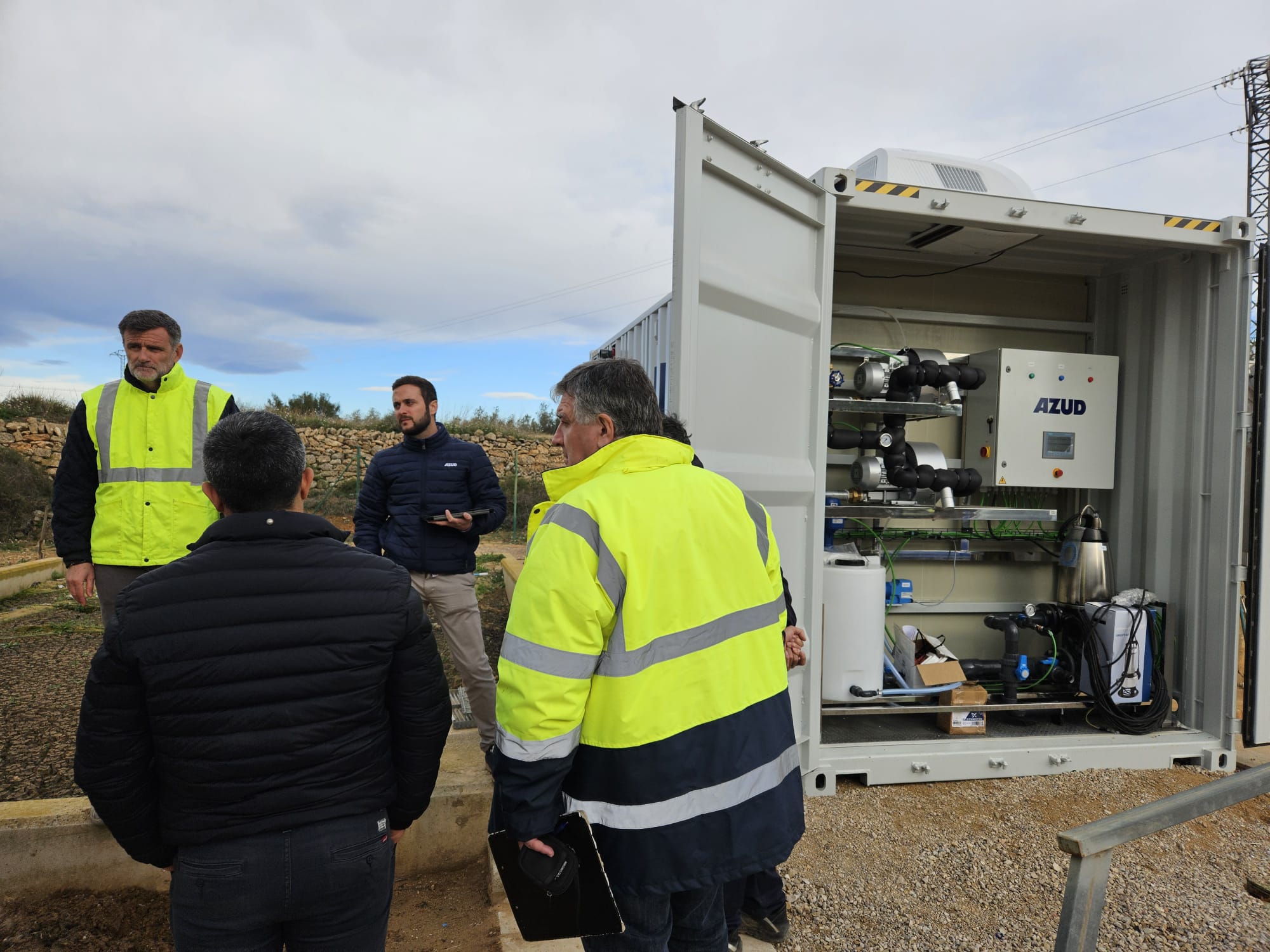
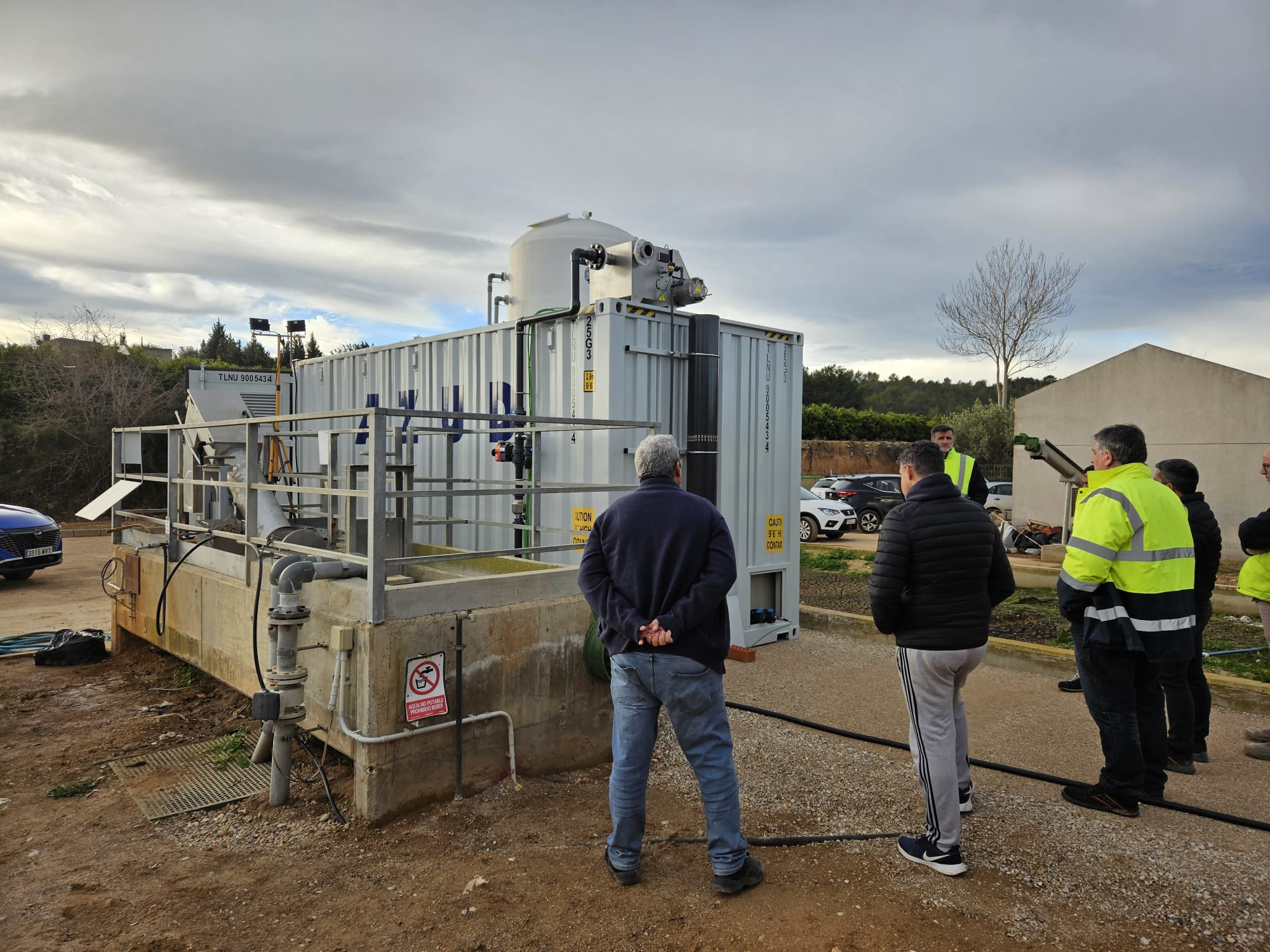
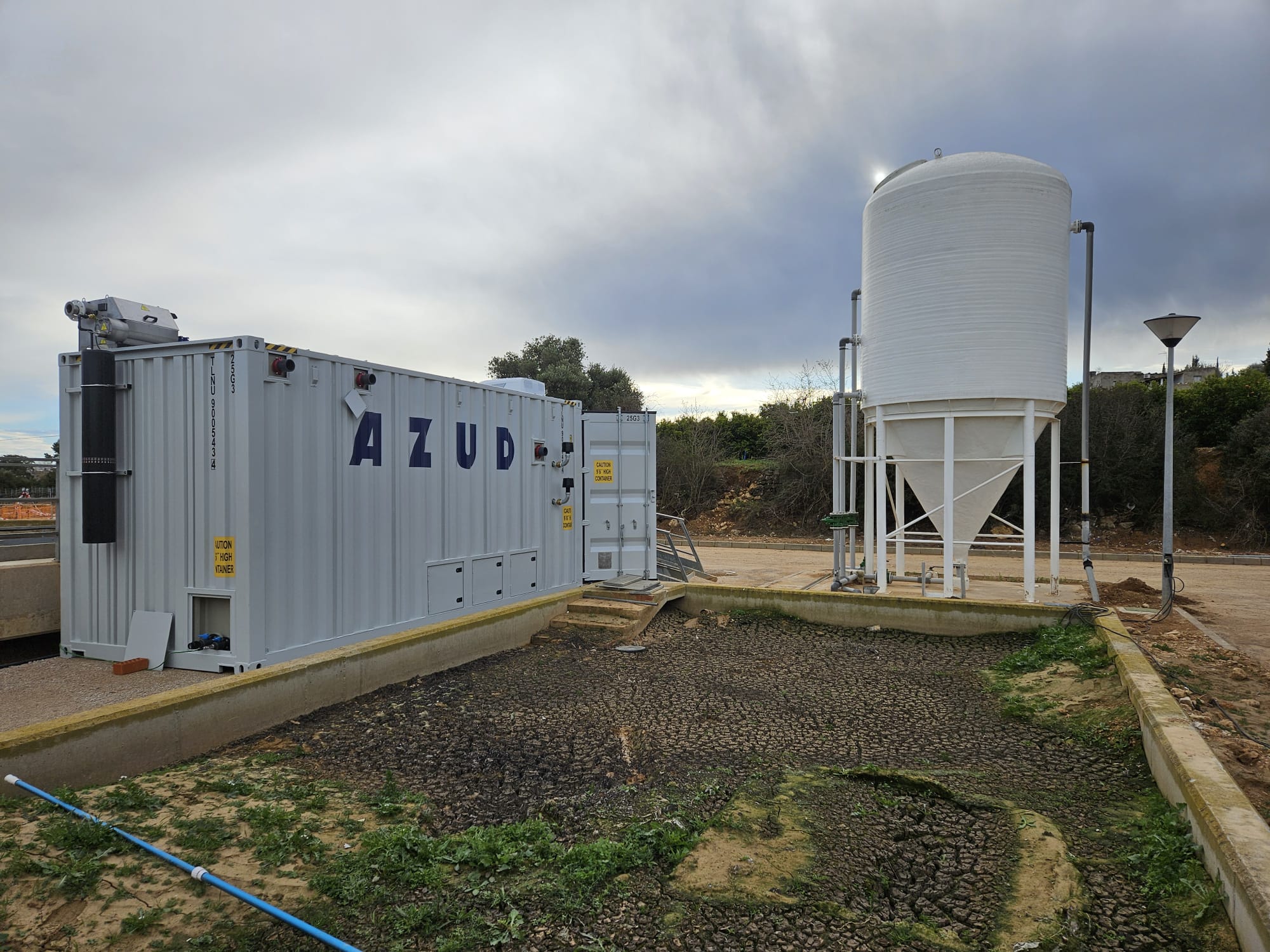
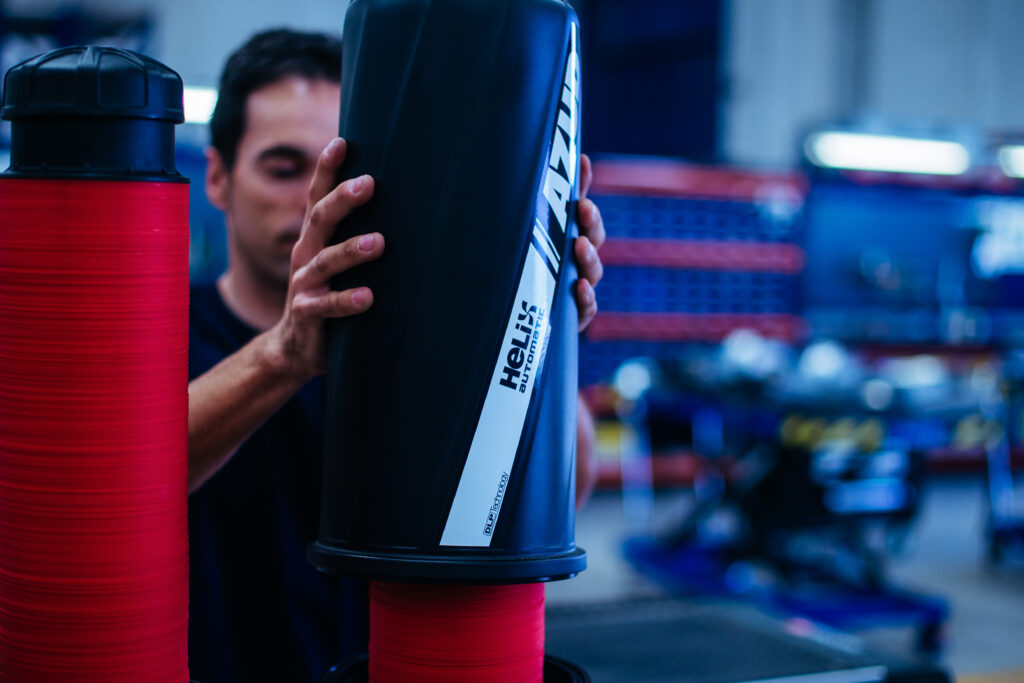
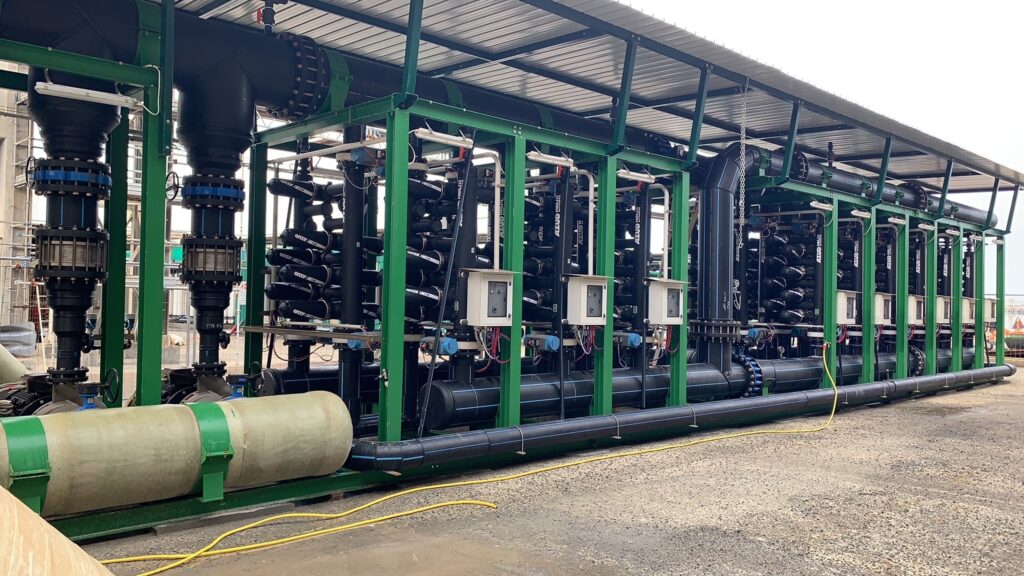
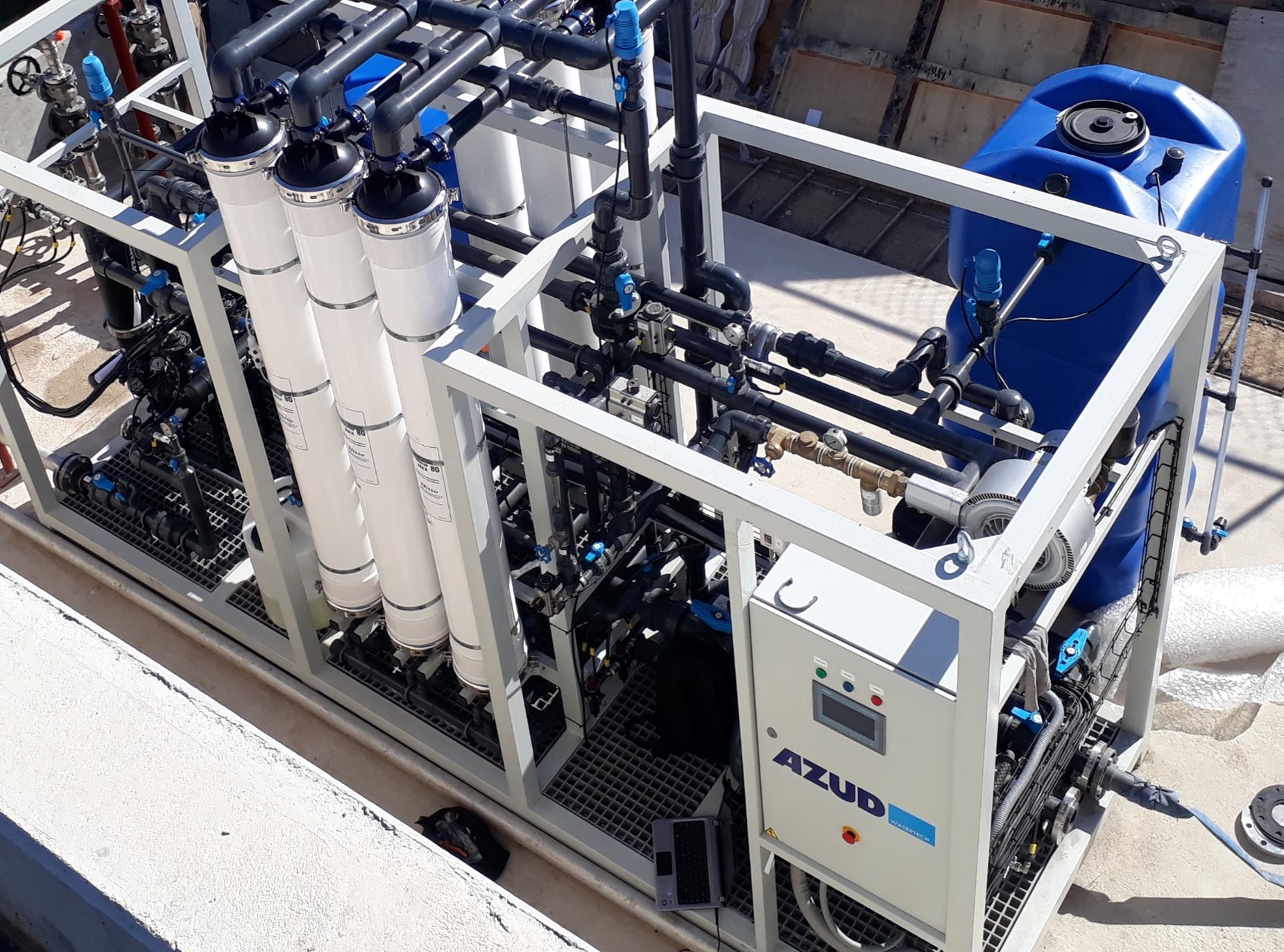
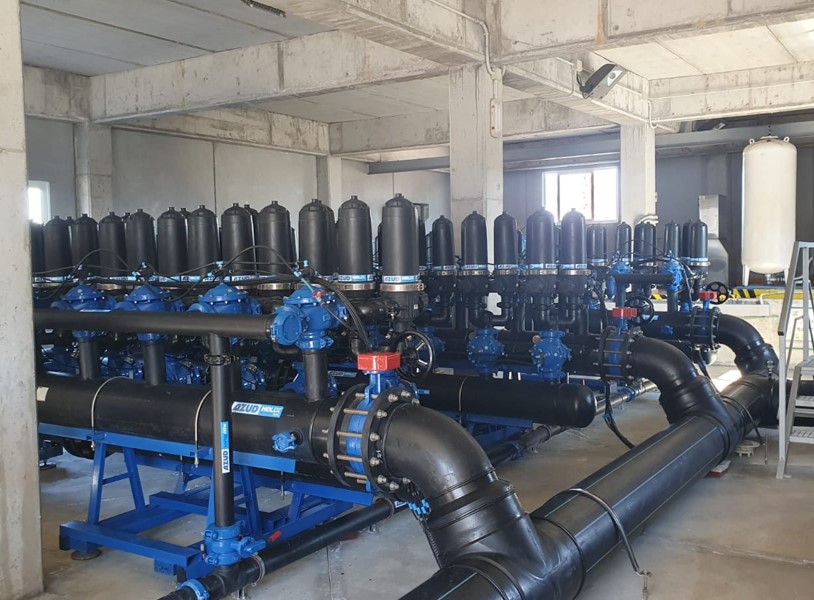
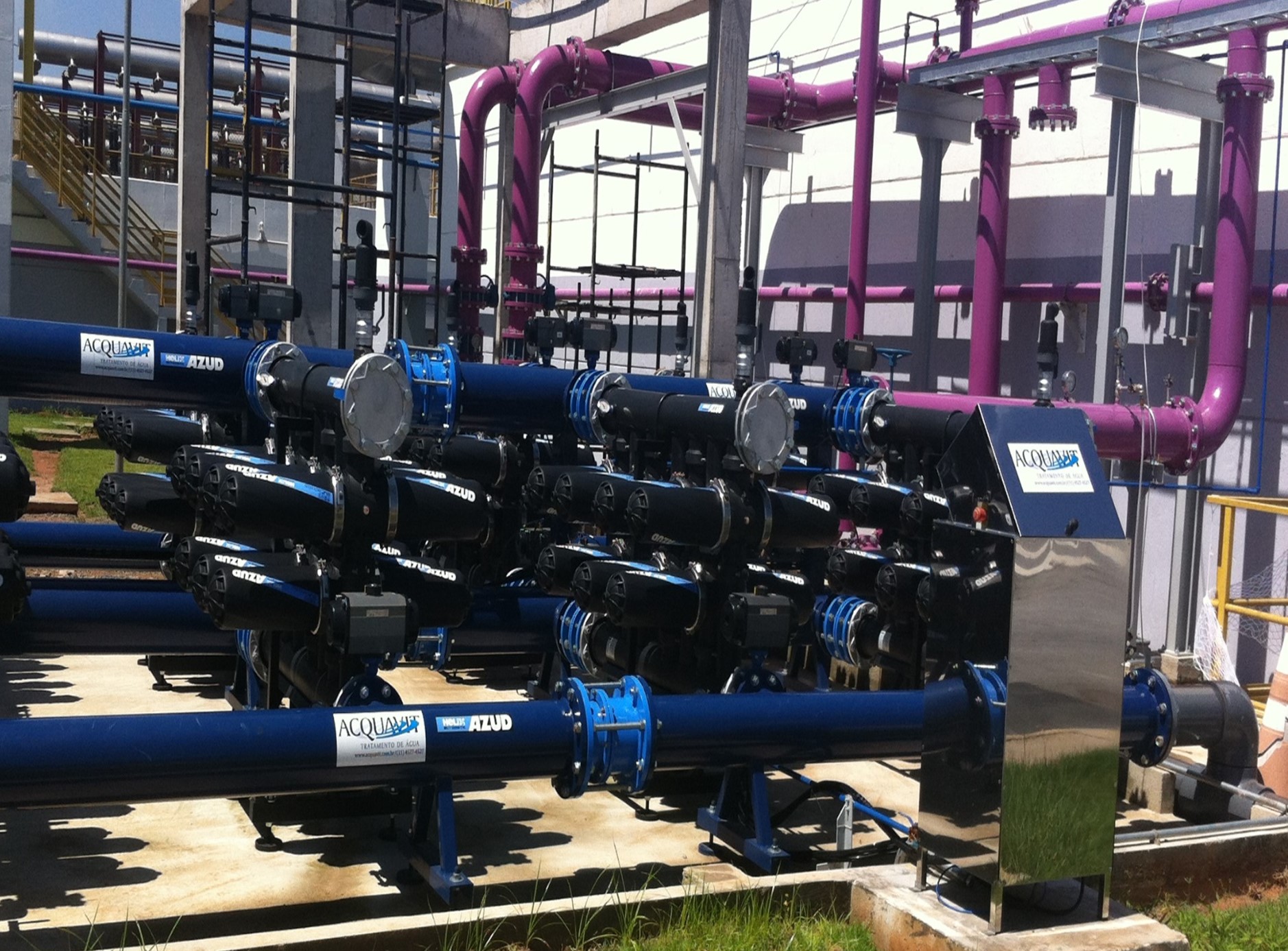
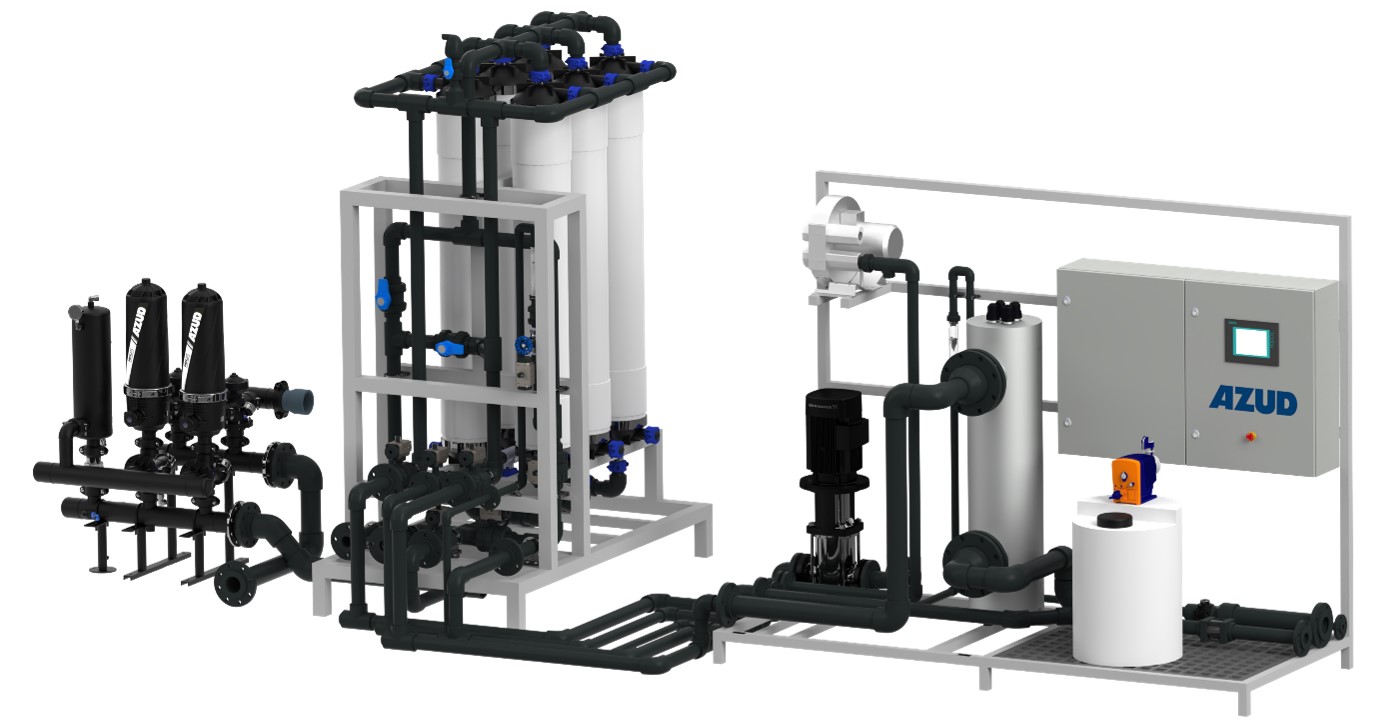
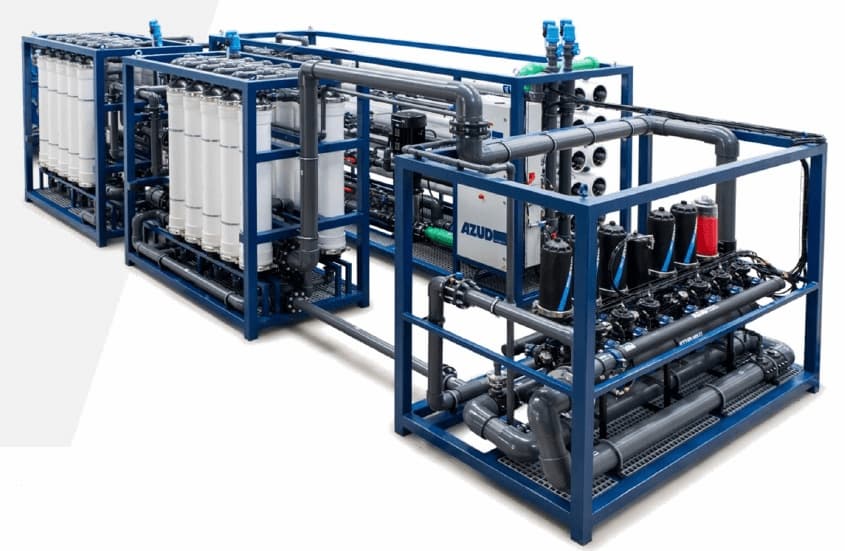
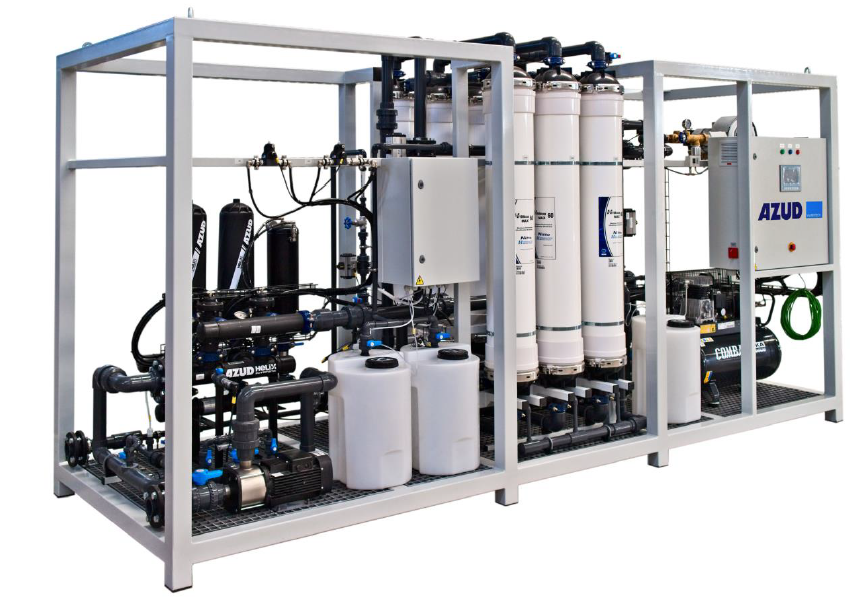
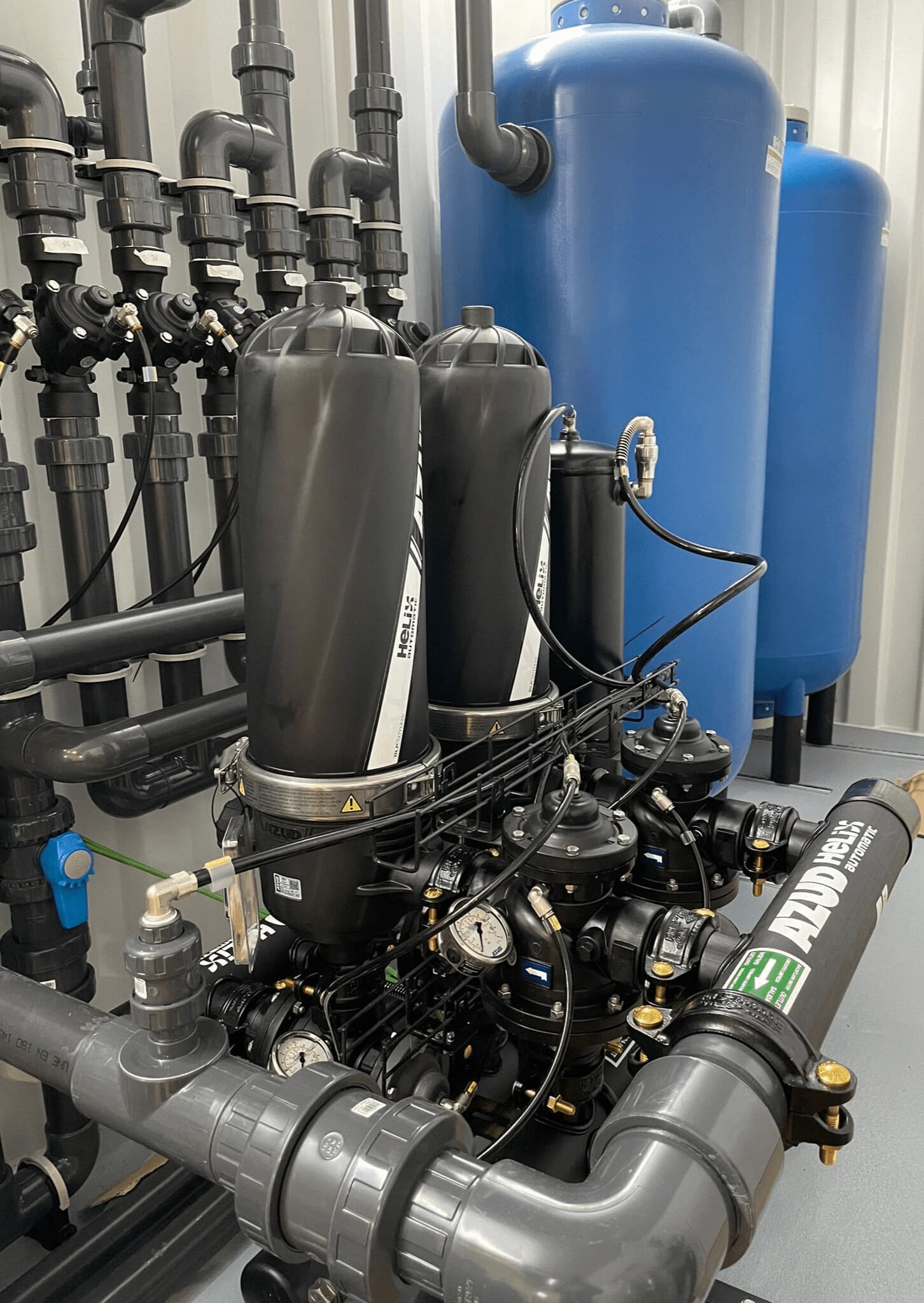
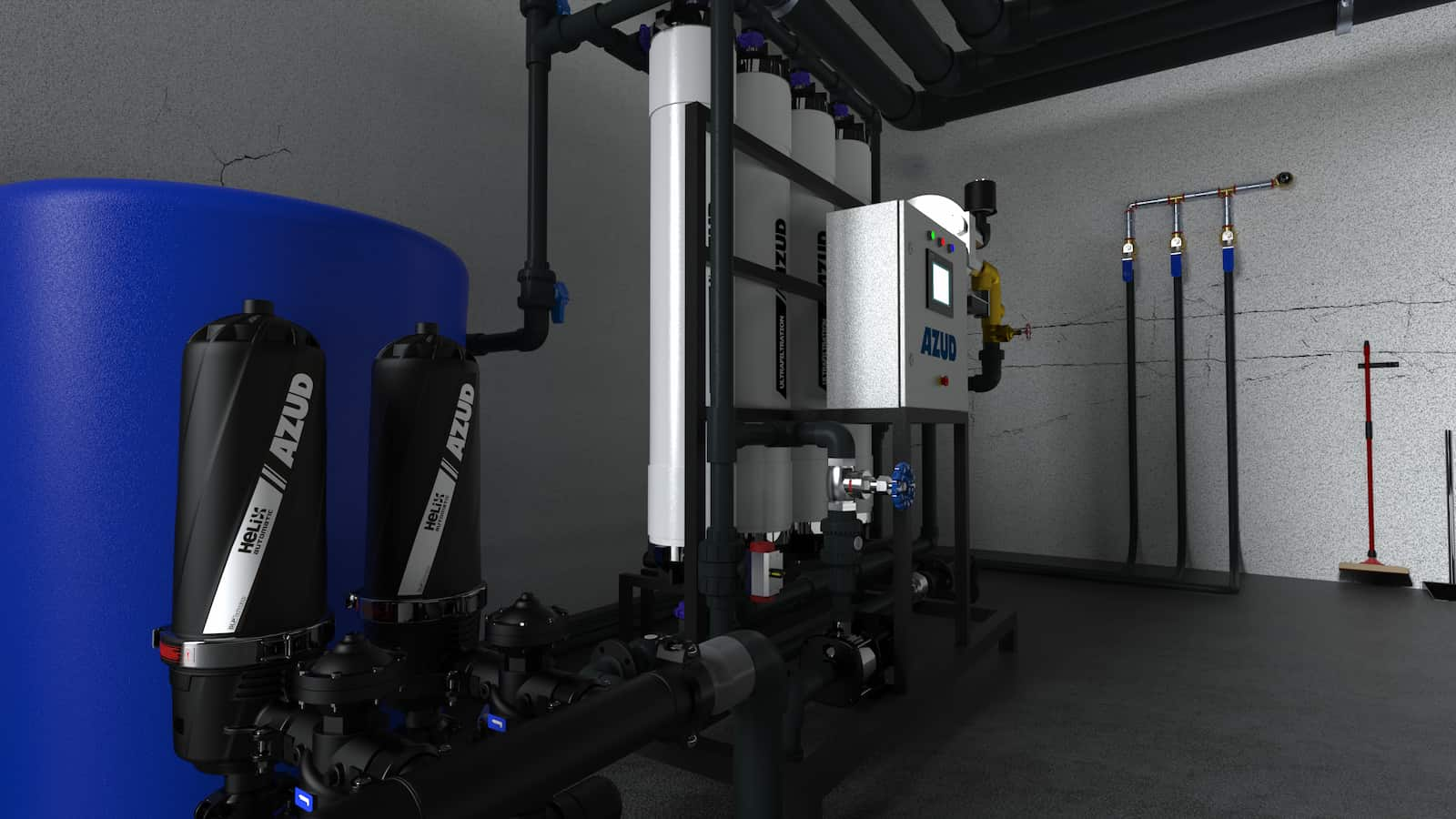
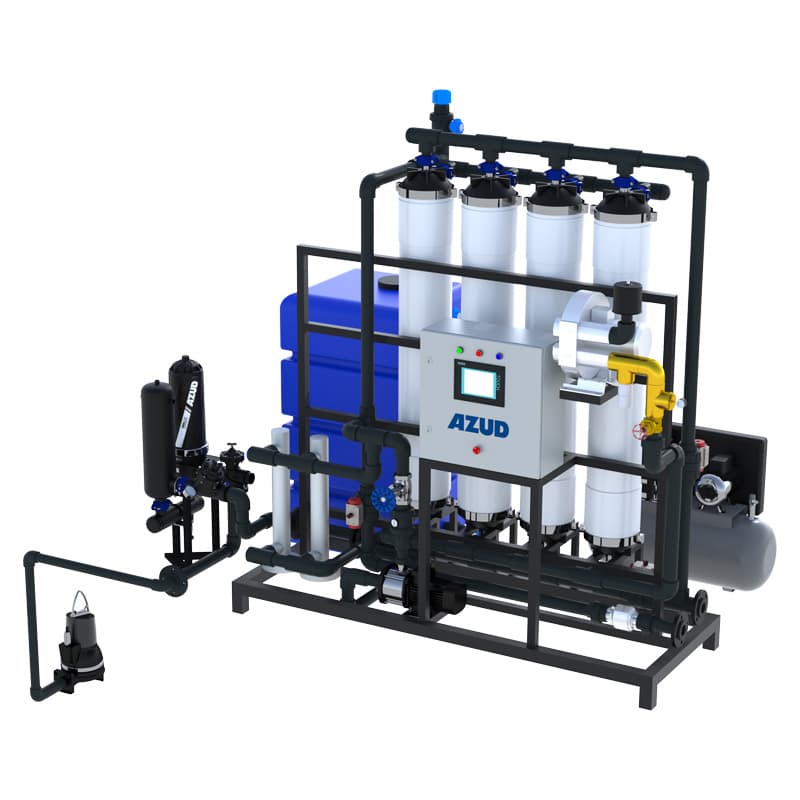
AZUD offers AZUD HELIX AUTOMATIC AA disc filtration systems to remove both organic and inorganic particles of very small micronage. These filtration technologies can be combined in several stages with different micronage levels, ensuring thorough water cleaning. In the first stage, suspended solids, both organic and inorganic, from the environment and fish can be removed. Then, in a subsequent stage, a finer cleaning is achieved, allowing complete removal of algae and smaller particles. In addition, it features an automatic air-assisted cleaning system that not only optimizes process efficiency, but also significantly reduces water consumption.
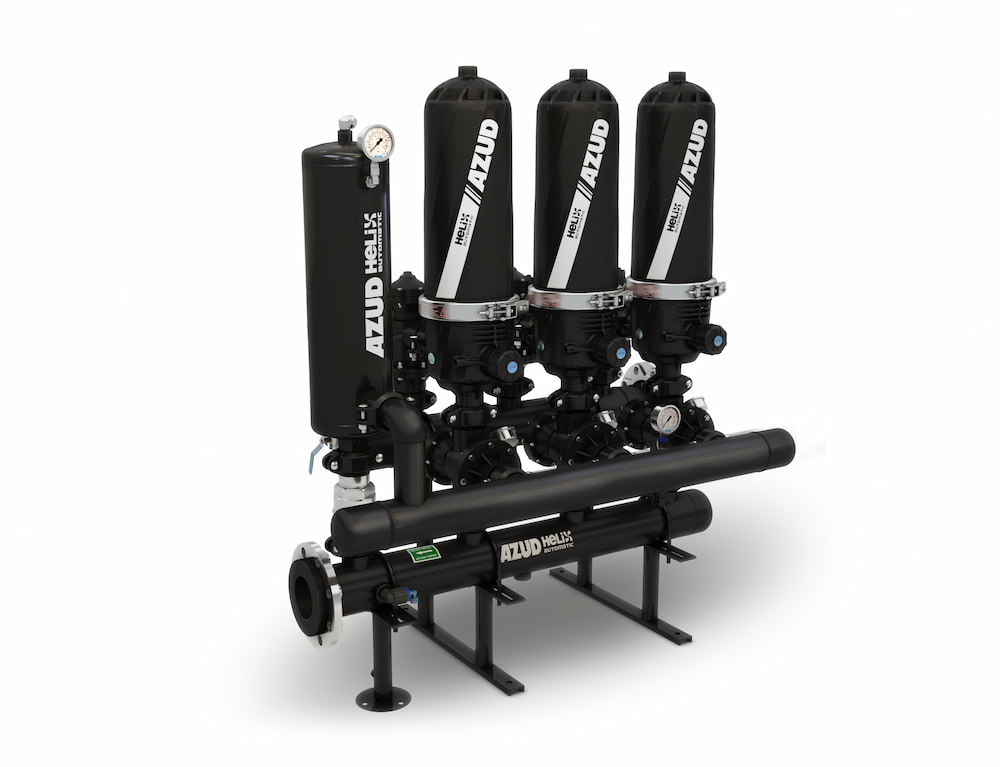

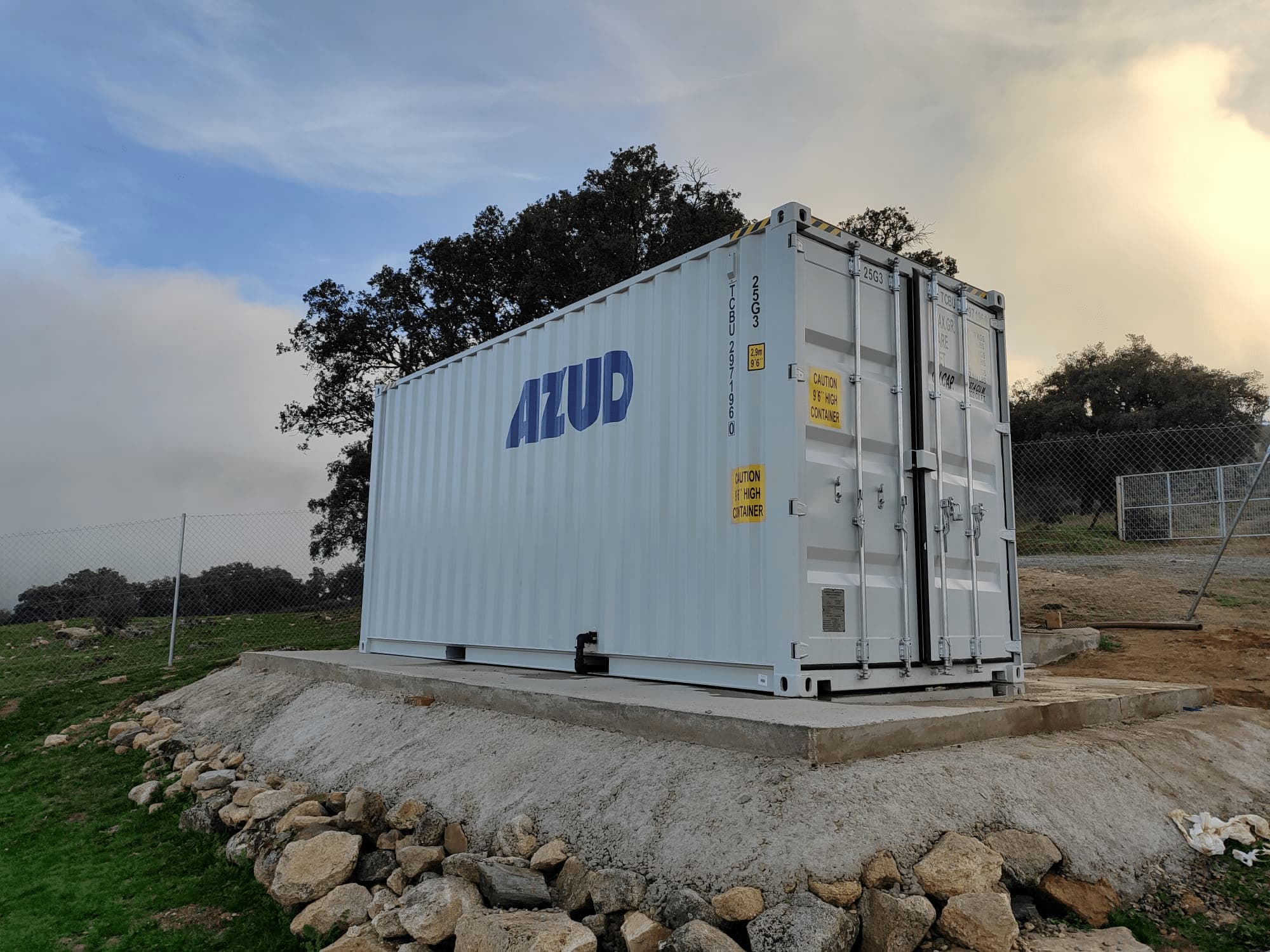
The combination of these technologies, together with other solutions, forms a comprehensive solution to ensure that the water meets ideal conditions. By incorporating disc filtration systems and complementing them with bed filters or ultrafiltration systems in a water treatment process, a highly efficient plant is obtained. These plants, designed in containers, offer significant advantages, such as compactness and modularity, which allows them to be adapted and conditioned according to the specific needs of each facility. This not only facilitates plant operation, but also protects the equipment involved.